Generative Tree
Catalan Architecture Image Classification
computer-vision cnn costum-kernel-design
A Catalan Architecture image classification model was developed using both deep learning and non-deep learning methods.
The multiclass classification problem involves the eight most frequently occuring styles in Catalunya.
The deep learning approach consideres fine tuning a convolutional neural network.
The non-deep learning approach encompasses extracting features from the images and training traditional machine learning models on the extracted features.
For more information be sure to visit the GitHub page. >
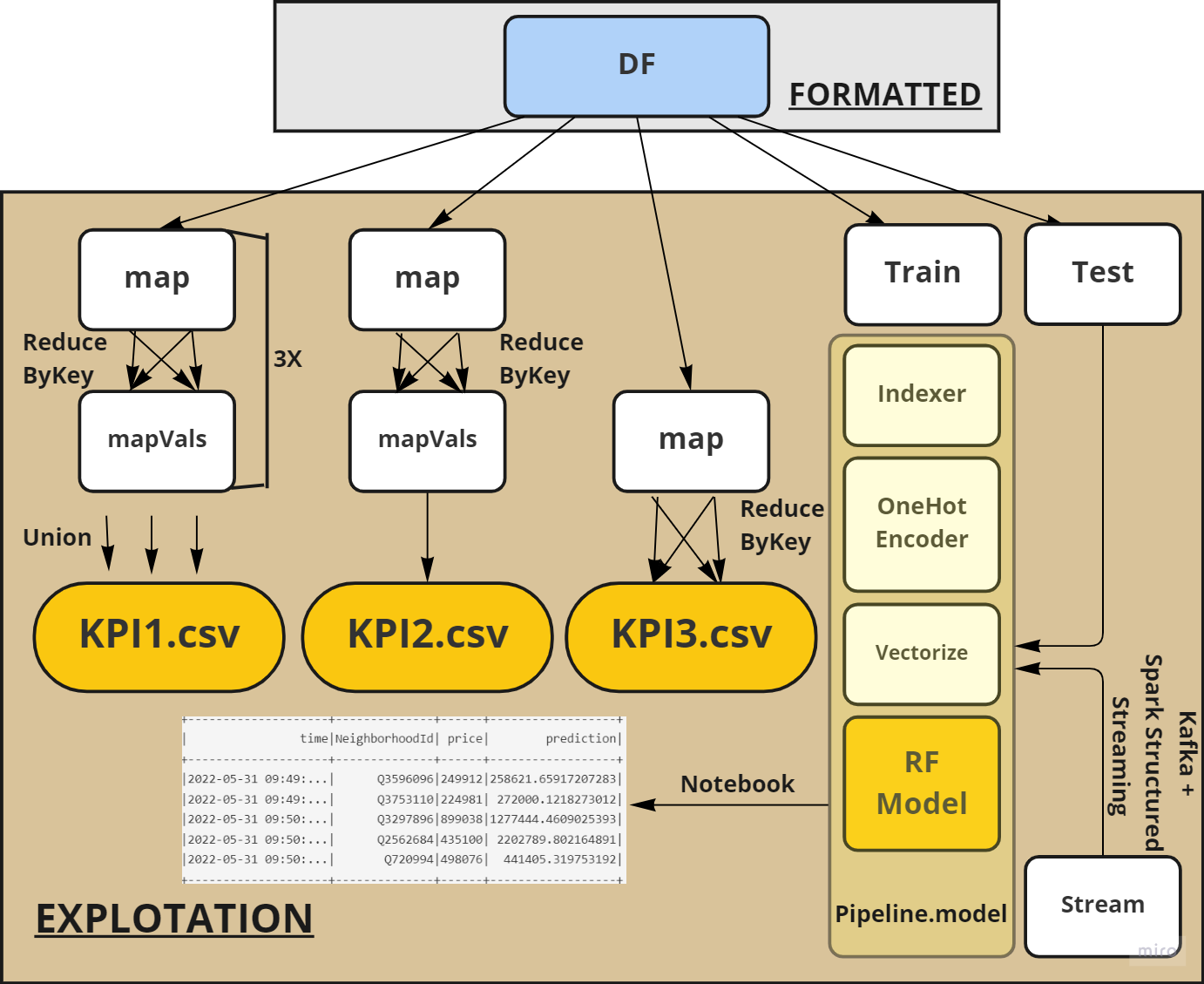
Big Data Pipeline
big-data spark distributed-storage distributed-processing
The goal of the project is managing and analyzing different housing data sources to emulate a complete Big Data pipeline. Various possible approaches and tools are explored
and reviewed in the report. The scope of the project is broad, ranging from data ingestion to distributed storage, analysis and stream ingestion.
For more information be sure to visit the GitHub page. >
Drug Neural NERC
nlp deep-learning transformers keras
Recognition and Classification of drug names with both traditional and non-traditional methods.
Both a CRF model and a Deep Learning model is build.
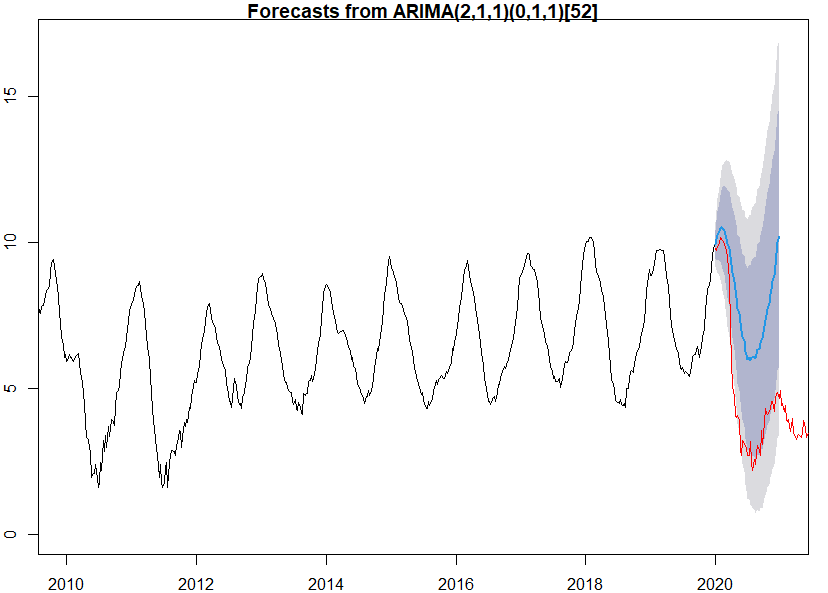
Influenza Time Series
time-series forecasting r
This time series analysis of USA flu data aims to identify patterns and trends in the data, estimate the underlying model of the data, validate the model using statistical techniques, use the model to make predictions about future flu trends, and identify and treat any outlying data points that may impact the analysis. The goal of this analysis is to better understand and forecast flu activity in the USA.
For more information be sure to visit the GitHub page. >
Bachelor's Thesis Physics & Astronomy
radioastronomy simulation 2d-regression
A cosmic ray air shower is a cascade of secondary particles as a result of a primary cosmic particle hitting
the Earth's atmosphere. This Bachelor's project aims to improve data analysis of these showers observed
by radio telescope network LOFAR and eventually SKA, which is still under construction, by implementing
new fit parameters to the current method. This method performs a two-dimensional regression of experimental data to simulation data to reconstruct the atmospheric depth of the shower, which yields information about its primary particle mass. Adding fit parameters like the length of the shower might improve
the accuracy of these property estimations. The thesis leans on both an understanding of the underlying
physics and data processing in python. The eventual report is structured as followed: A theoretical background of the physics involved, a summary of the current fitting routine, a description and analysis of the
new method and lastly its potential implications for LOFAR and SKA. Here you can download the full paper. >